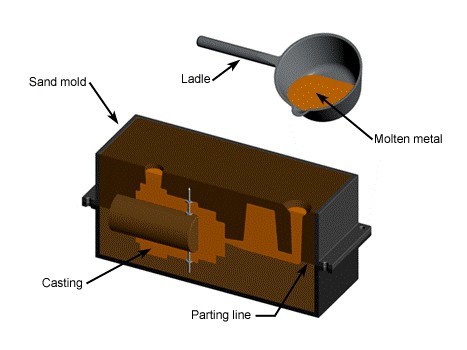
Sand casting is highly suitable for creating single pieces as well as small and medium batches. With aluminum Sand Casting, the most complicated casting can be produced in an extremely efficient and precise manner.We distinguish ourselves by using natural form sand instead of synthetic sand. This results in a smoother and sleeker surface with great dimensional accuracy and reproducibility.
Sand casting remains one of the most cost-effective and high-efficiency metal casting processes, in which sand is employed as the mould material to create custom designs and complex metal parts. The sand molds themselves are expendable after production, and sand mould casting process works with nearly any metal alloy to produce a wide variety of custom parts with complex geometries. Sand casting produces parts ranging from very small weight (less than a pound) to very big tons.
(More content reference:Sand casting – Wikipedia).
Precise Cast is a premier global sand casting manufacturer based in Qingdao City that offers a wide range of high-quality metal casting services, striving to only deliver the best quality sand casting products. Our sand mold casting foundry makes use of high quality raw materials, skilled foundry workers, state of the art machines and cost-efficient casting techniques.
There are mainly eight steps of sand casting process:

Designing patterns is a complex process that requires very specific know-how.Our technical team can help design a reusable pattern before creating the mold, which helps plan the mold and product details greatly. Usually the new pattern allows for some thermal contraction during sand casting process.
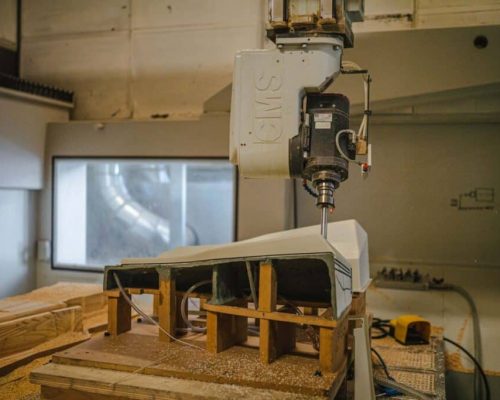

Patterns made of wood, resin (plastic) or aluminium could be used to produce during the casting.The best component starts with a qualified and experienced casting pattern maker. Our highly skilled patternmakers create custom patterns based on your exact specifications.
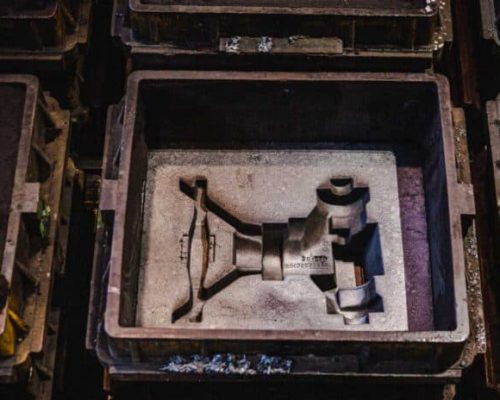

We must prepare for the molten metal to be poured after the sand casting mold has been made. The surface of the mold cavity is lubricated to facilitate the removal of the casting. The cores are positioned and the mold halves are closed and securely clamped together. It is essential that the mold halves remain securely closed to prevent the loss of any material. These gating and riser features ensure the molten metal alloy can entirely fill the mold cavities before they start to harden and that no complex detailing remains hollow or half-formed.
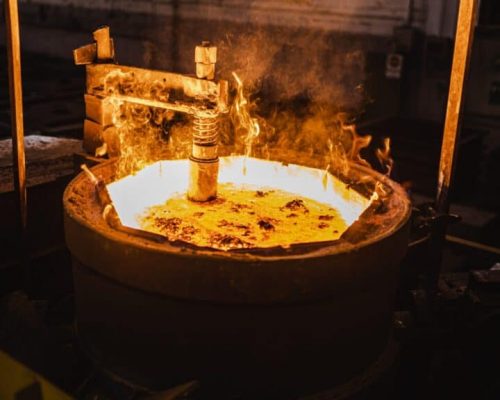

Without this process of melting, production of many superalloy and complex alloy castings would be extremely difficult or impossible.
Electrical furnaces are used to melt iron from scrap and the necessary alloys or additional components needs to achieve the desired final standard.
Often the metal used is an alloy, or a mixture of elements that, together, provide optimal mechanical properties. Melting processes vary: in its simplest form, melting consists of placing alloy in a receptacle with a higher melting point and heating it over a burner or open flame. More contemporary melting methods, like induction melting, rely on the physical properties of alloys to melt them and bring them to casting temperature more efficiently.
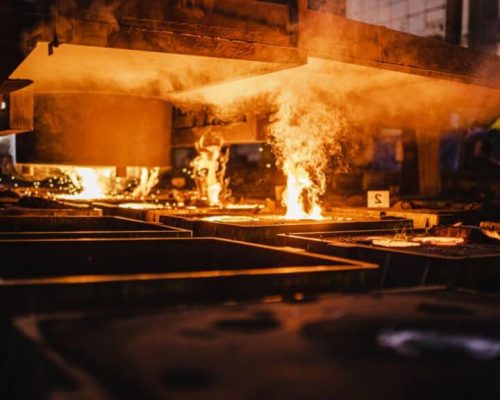

The molten metal can be ladled from its holding container in the furnace and poured into the mold. The in-mold metal delivery system will fill both the product portion and the gating and risers of the mold. The pouring process can be operated manually or by an automated machine. Enough molten metal must be poured to fill the entire cavity and all channels in the mold. The filling time should be very short in order to prevent early solidification of any part of the metal.
After melting, the mold is moved to a cooling area where the sand casting parts will be left to cool and solidify. Some sand casting manufacturers also adopt quenching baths, applied to enable the rapid cooling of castings. In some cases, the rapid cooling process also results in the forming of certain metallurgical properties.
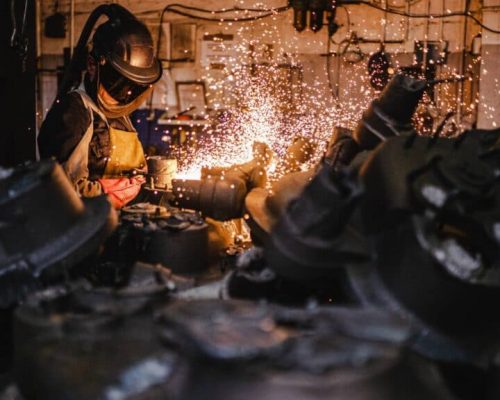

Castings will be removed either manually or by making use of vibratory tables after cooling step finished. Vibratory tables are used for shaking refractory materials away from the casted parts.Trimming involves cleaning and removing the section that connected to the main part such as runner, sprue etc.
The molten metal from the channels in the mold solidifies attached to the part during cooling process. These excess materials must be trimmed from the casting either manually via cutting, sawing, polishing, or trimming press. The time of trimming the excess material can be estimated from the size of the casting’s outline.
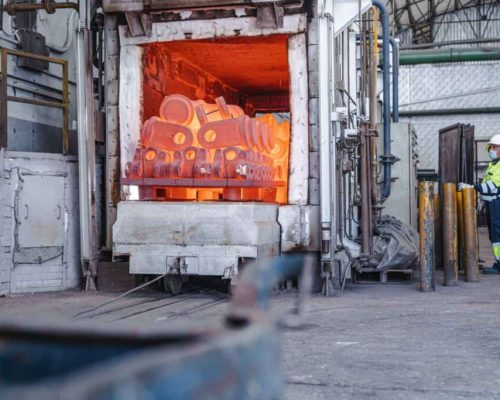

In the final stage, manufacturers apply all of the finishing steps to get the part ready for assembly or packing before delivery, which includes cutting away the gates, risers, and runners, sand-blasting or grinding the metal to the required degree of smoothness, and other necessary machining processes.

Then the casting parts will be fully tested for the dimensions, surface, mechanical properties and other required tests before packing and delivery.
For more details, you are welcome to visit our quality inspection standard.
Greensand molds use a mixture of water, clay sand or binder. Typical green sand mixtures contain 7% clay, 4% water, and 89% sand, thus providing the proper levels of strength, permeability, reusability, and collapsibility desired for sand casting projects. Greensand molds are the least expensive and most widely used method for sand casting parts.
A skin-dried mold starts like a greensand mold, after then additional binders are added and the cavity surface is dried by a torch or heating lamp to increase mold strength, which also improves the dimensional accuracy and surface finish, but the collapsibility will be lowered. Dry skin molds are more expensive and require more time, thus lowering the production rate than greensand molds.
shell molding uses a mixture of dry, fine silica sand to create casts with smooth finishes. Foundry workers mix this sand with 3–8% thermosetting resin and minimal clay content and then drop it onto a heated pattern plate, creating a thick (6 mm) shell that they then heat for several minutes to cure the shell. The shell mold has higher accuracy in dimension, but it is also expensive and results in a lower production rate.
This sand casting process involves the use of chemical binders to bond the molding sand and hardens at room temperature. Heating is not necessary for this process, which is also called Air set molding.
Large parts can be produced.
Complex shapes can be cast easily.
Large selection of metal to choose from.
Tooling and equipment cost is low compared to some other metal forming processes.
Scrap metal can be recycled.
Short lead compared to other similar processes.
Our green sand casting services are present in a wide variety of products,including high quality,top performance industrial parts.We typically serve the following industries:
✔Rail trains
✔Automotive
✔Heavy Duty Trucks
✔Public Works
✔Agricultural Equipment
✔Defence
✔Ship Construction
✔Lifting
✔Oil&Gas
✔Construction Equipment
✔Mining
✔Hydraulics
✔Wind Energy
✔Machining Equipment
If you’re interested in getting a quote for your upcoming sand casting projects, contact Precise Cast today.
We’re happy to discuss our casting processes and other metal fabrication solutions you may be interested in.